Create an environment
How to create a new custom environment from a Docker build script
Step-by-step tutorial
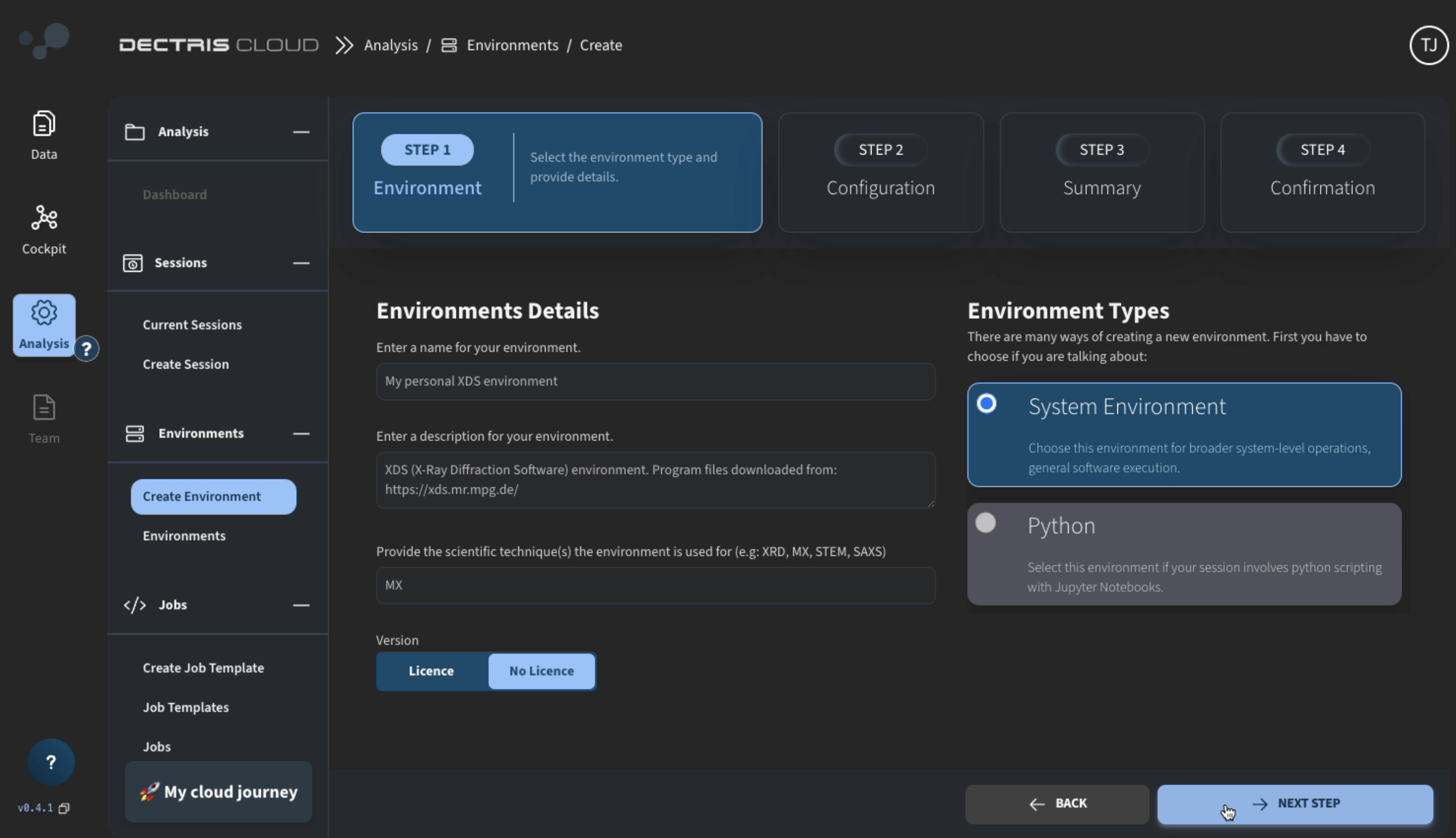
- Navigate to the creation page via Analysis → Environments → Create Environment
- Enter environment details such as title, description, and intended scientific technique:
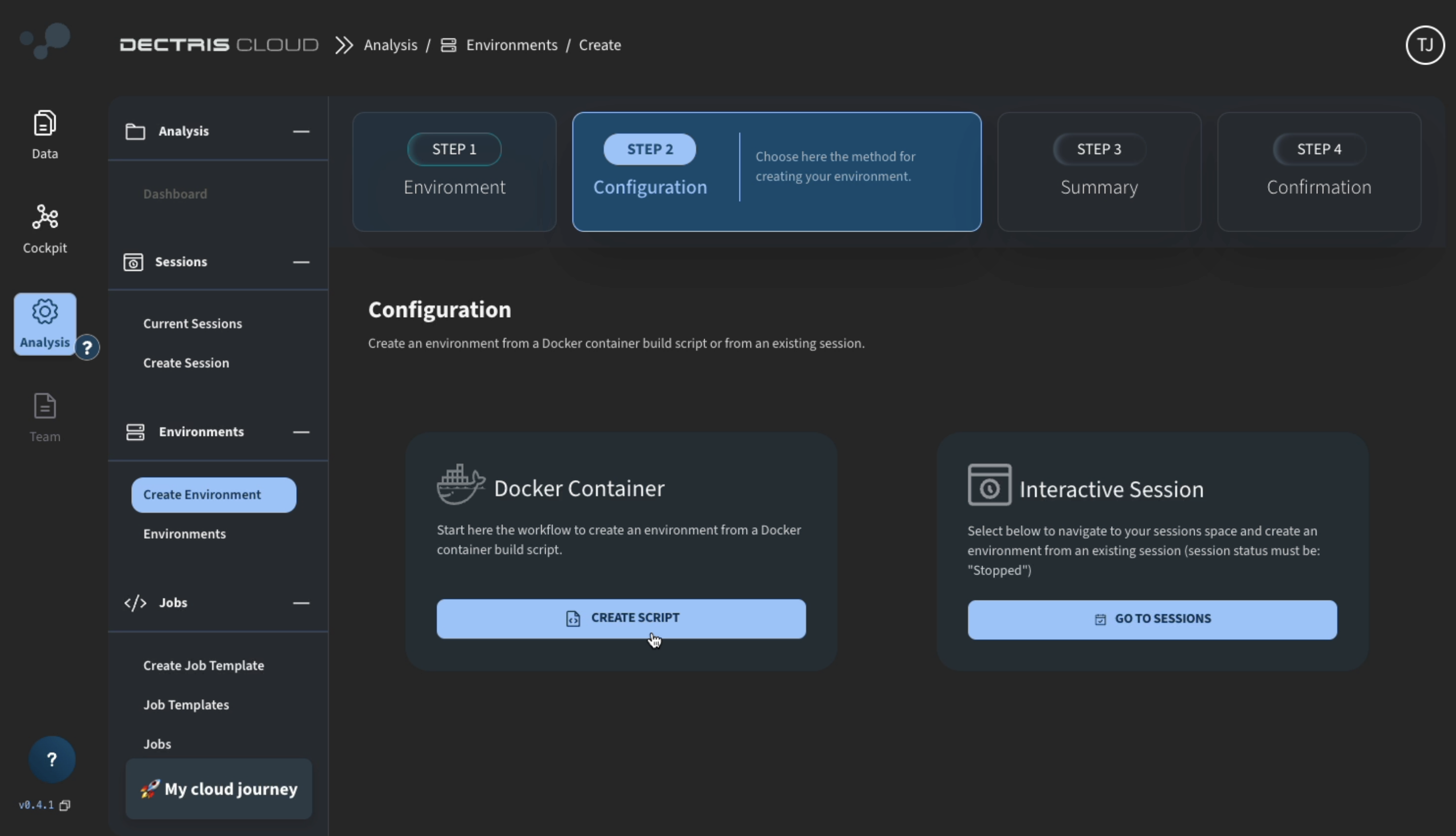
- On the next page, click CREATE SCRIPT:
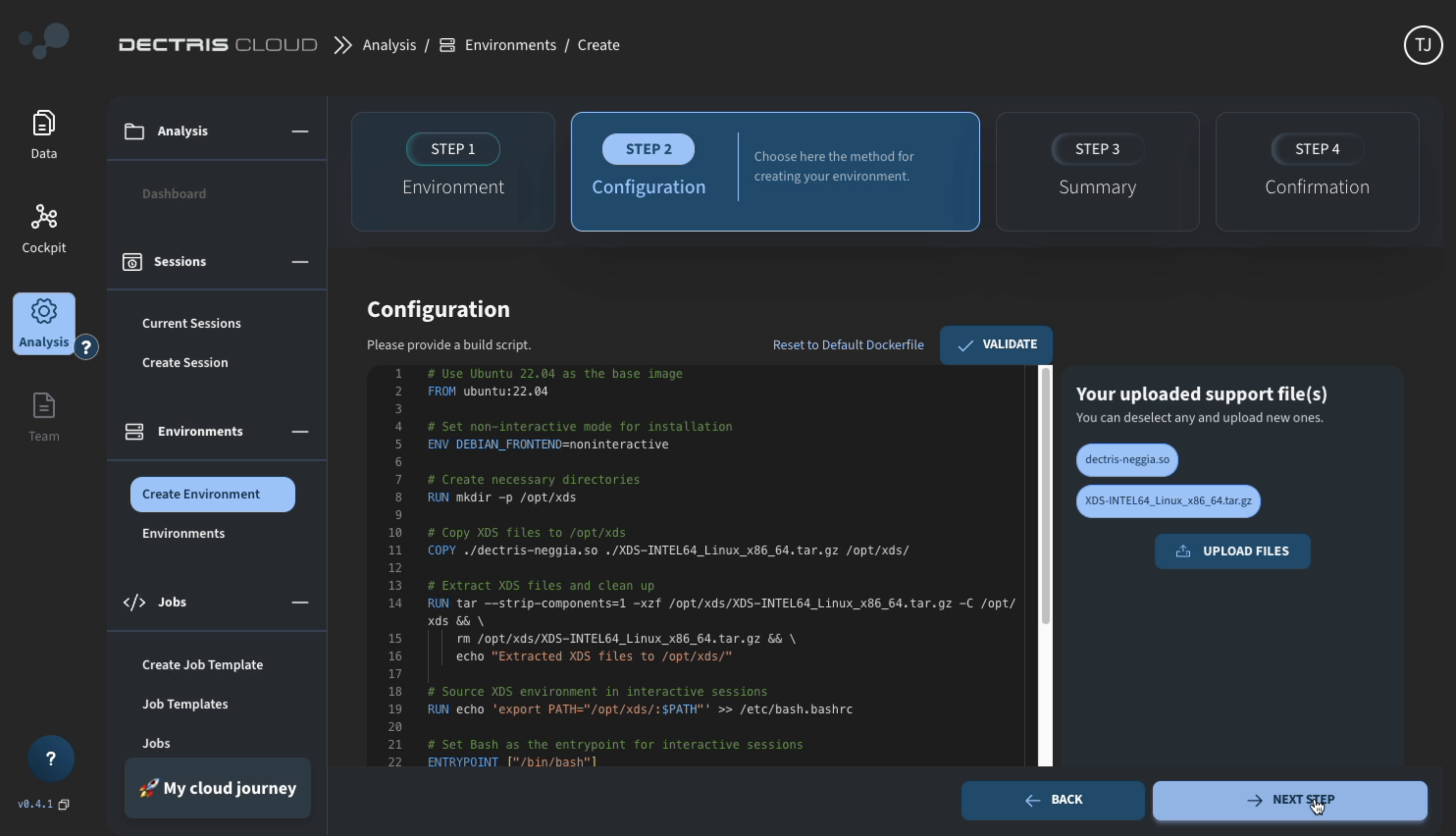
- Write (or copy-paste) a Docker build script into the editor, keeping the following in mind:
- Currently, only ubuntu:22.04 and ubuntu:24.04 are available as a base image
- If you upload a supporting file,
script.sh, you can copy the file into the container from the./script.shlocation - Note that the
ENVcommand will set an environment variable while the environment is created, but it will not be set in a session started with this environment. E.g., to/your/dironPATH, it is recommended to use bothENV PATH=$PATH:/your/dirandRUN echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/your/dir' >> /etc/profile
- Do NOT add any files to
/appor/workas those directories will not be accessible when running a job.
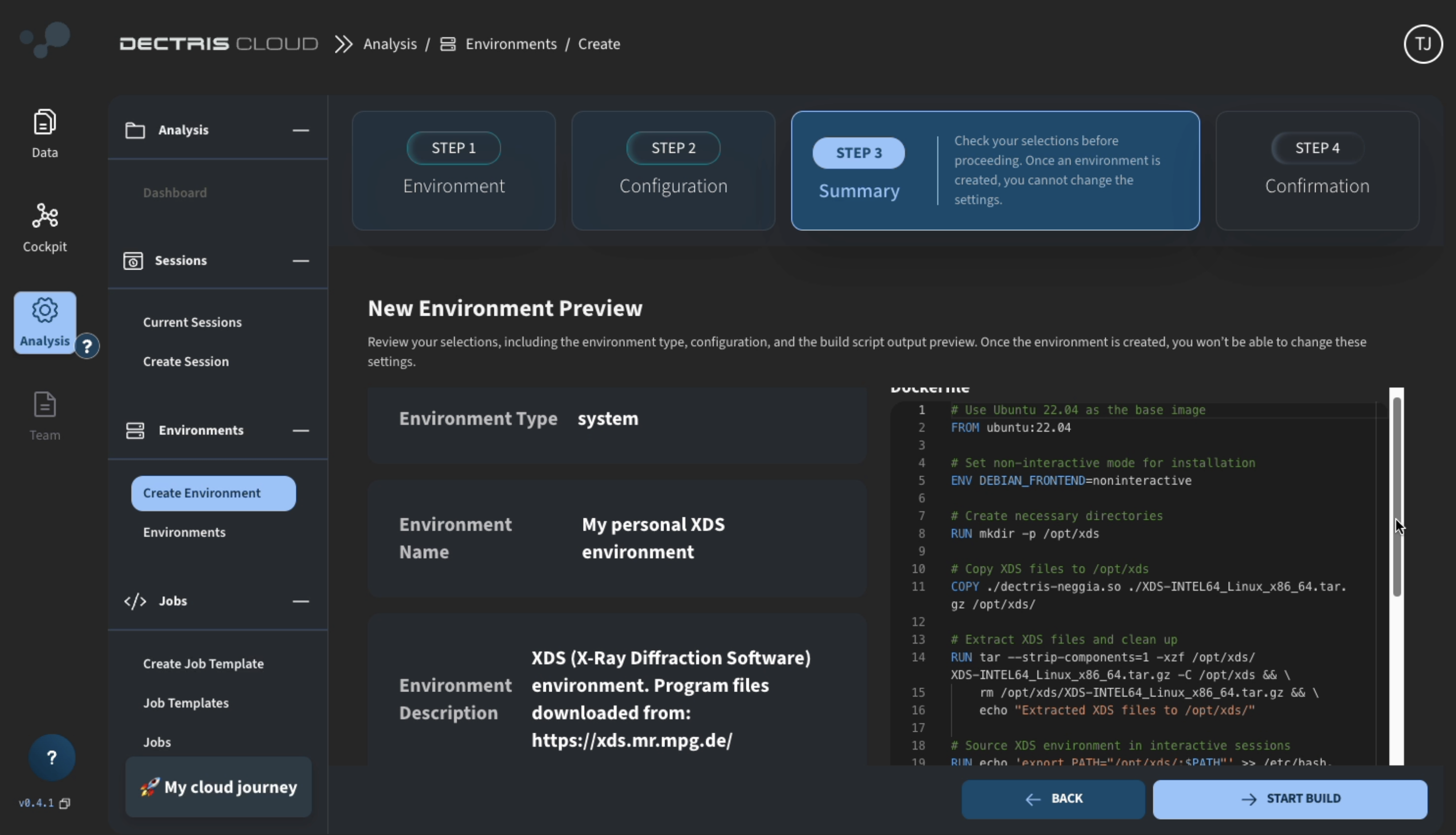
- On the next page, review your environment configuration and click START BUILD:
- On the build confirmation page, you can either wait for the environment build to finish to review the build output:
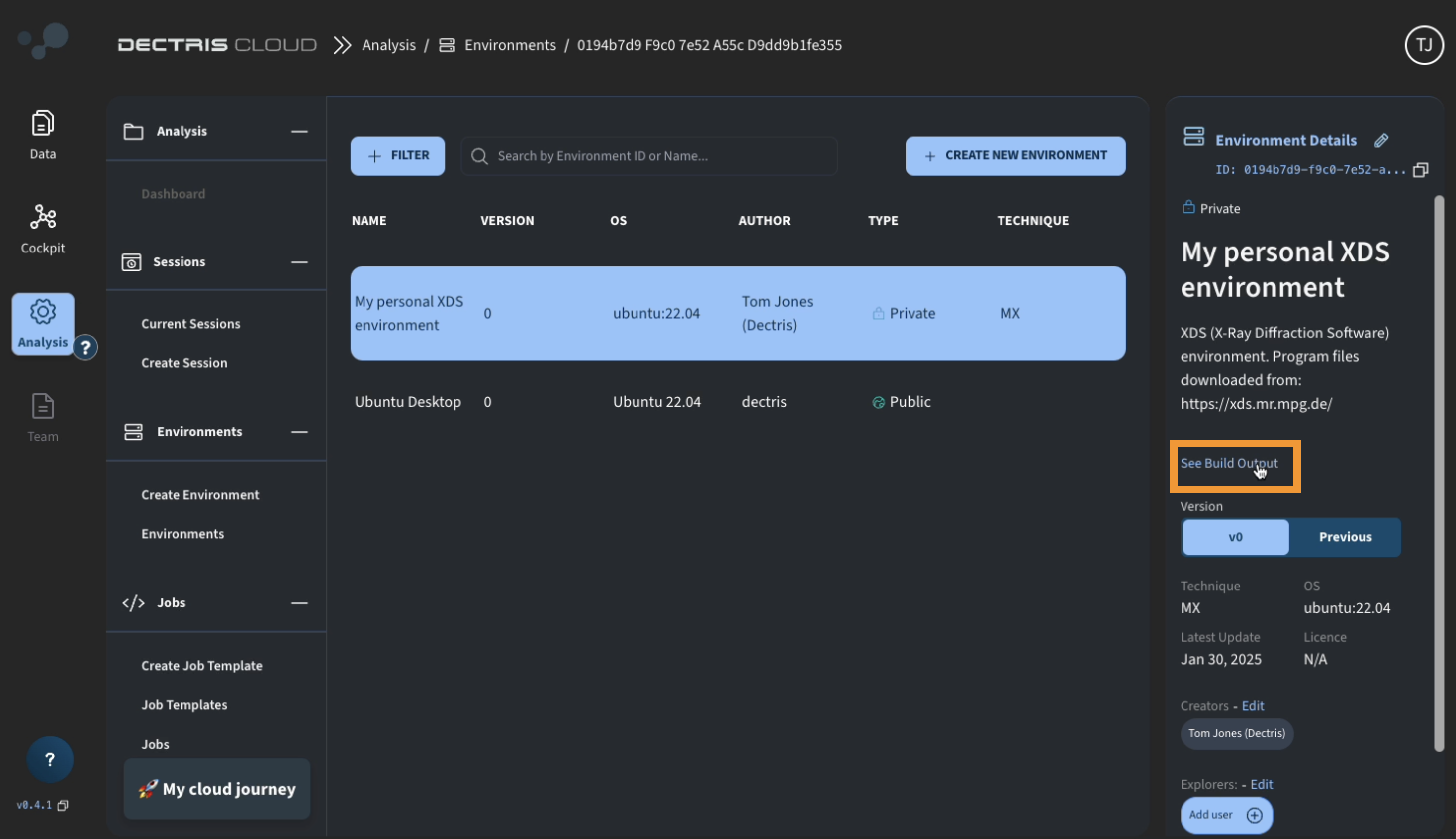
or you can navigate to the environments overview table at Environments → Environments, choose your newly created environment, and review the build output from there:
- Environments can be used personally for starting sessions with specific configurations and/or launching jobs. They can also be shared with collaborators. Before sharing an environment, make sure you have the rights to redistribute any software within it.
CloudPlay
References
[1] https://xds.mr.mpg.de/
[2] https://github.com/dectris/neggia